The Ultimate Guide to Data Security Standards
Learn about the data security standards enterprises incorporate into their IT asset recovery programs

Over the past few years, many companies have adapted to a hybrid work environment, allowing employees to work remotely by issuing them corporate-owned mobile devices.
As enterprises deploy an increasing number of IT assets, their IT teams quickly realize they do not have an effective way to deploy, support, and recover IT assets aside from manually tracking details in a spreadsheet. This lack of process unveils several IT asset program security gaps and risks. Organizations must address gaps in data security because of a significant increase in cybersecurity incidents in the last few years.
Additionally, as more employees use corporate-issued mobile devices to access company networks, companies’ IT asset recovery needs will increase, given devices—both deployed and retired—must be recovered with every upgrade or employee separation. Organizations should have a secure IT asset recovery solution in place to keep up with increasing demand and protect valuable company data. Without the proper measures in place, entire corporations are at risk.
If you’re looking for a solution to keep up with recovery program demands, or if you wonder if your organization has the appropriate security standards in place for your IT asset recovery programs, you’re in the right place.
This guide will discuss the best practices in data security standards for enterprises—like DoD 5220.22-M and NIST 800-88 data destruction standards, ISO certifications, encryption and cryptographic erasure, SERI and R2 certification and guidelines, and SOC 2 Type 2 audits and attestation reports.
Keep reading to learn more, or navigate the links below to jump ahead.
DoD 5220.22-M Data Destruction Standards
What is DoD 5220.22-M?
DoD 5220.22-M is a data destruction standard established by the United States Department of Defense. DoD 5220.22-M is the most common, readily available, and basic “standard” for any data destruction process.
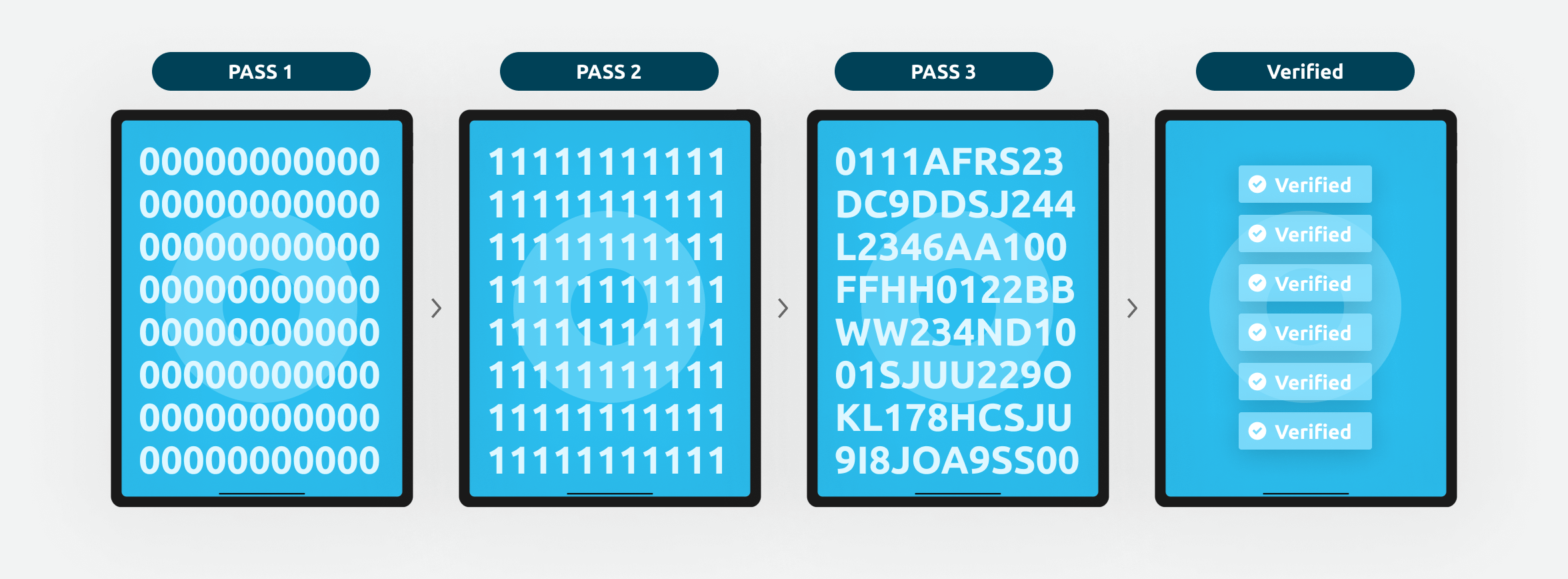
DoD 5220.22-M is a specific process that ensures the destruction of data on hard disk drives (HDDs) and, therefore, the permanent destruction of data from a device before the device is redeployed, resold, or disposed of for recycling. This process only applies to HDDs and requires overwriting HDDs with patterns of ones and zeros in three (3) secure overwriting passes, including verification at the end of the final pass. For example:
- Pass 1: Overwrite all addressable locations with binary zeroes
- Pass 2: Overwrite all addressable locations with binary ones, complimenting Pass 1
- Pass 3: Overwrite all addressable locations with a random bit pattern
- Verify the final overwrite pass
- Physical destruction of devices when necessary
The History of DoD 5220.22-M Data Destruction
The DoD 5220.22-M method for data destruction first appeared in 1995—long before the widespread usage of smartphones, tablets, laptops, and smart devices.
In 2001, a variation of the DoD 5220.22-M method became available and accepted for use. This new method—known as the DoD 5220.22-M ECE method—included seven secure overwriting passes.
Although the DoD 5220.22-M ECE method provided organizations with a different level of data destruction that can be performed, a version of DoD data destruction hasn’t been specified as preferred.
DoD 5220.22-M had its last major update in 2006. Although the DoD 5220.22-M method is outdated and no longer serves as the most recommended level of data destruction, since it was a standard established by the Department of Defense, it still carries a great level of credibility. IT teams may still implement DoD 5220.22-M data destruction methods in their security policies.
NIST 800–88 Data Destruction Standards
What is NIST 800–88?
NIST 800–88 refers to the National Institute for Standards and Technology (NIST) Guidelines for Media Sanitization. It is the most updated and recommended level of data destruction in any industry.
With NIST 800–88, data is unrecoverable after one overwrite. NIST 800–88 allows organizations to save time and labor while increasing security, because undergoing several overwrites—such as with DoD 5220.22-M—can be laborious and time-consuming.
NIST 800-88 universally applies to technology and other media types—even those that may not have been invented yet. It also considers both storage systems for devices—hard-disk drives and solid-state drives—making it applicable to a broader range of devices.
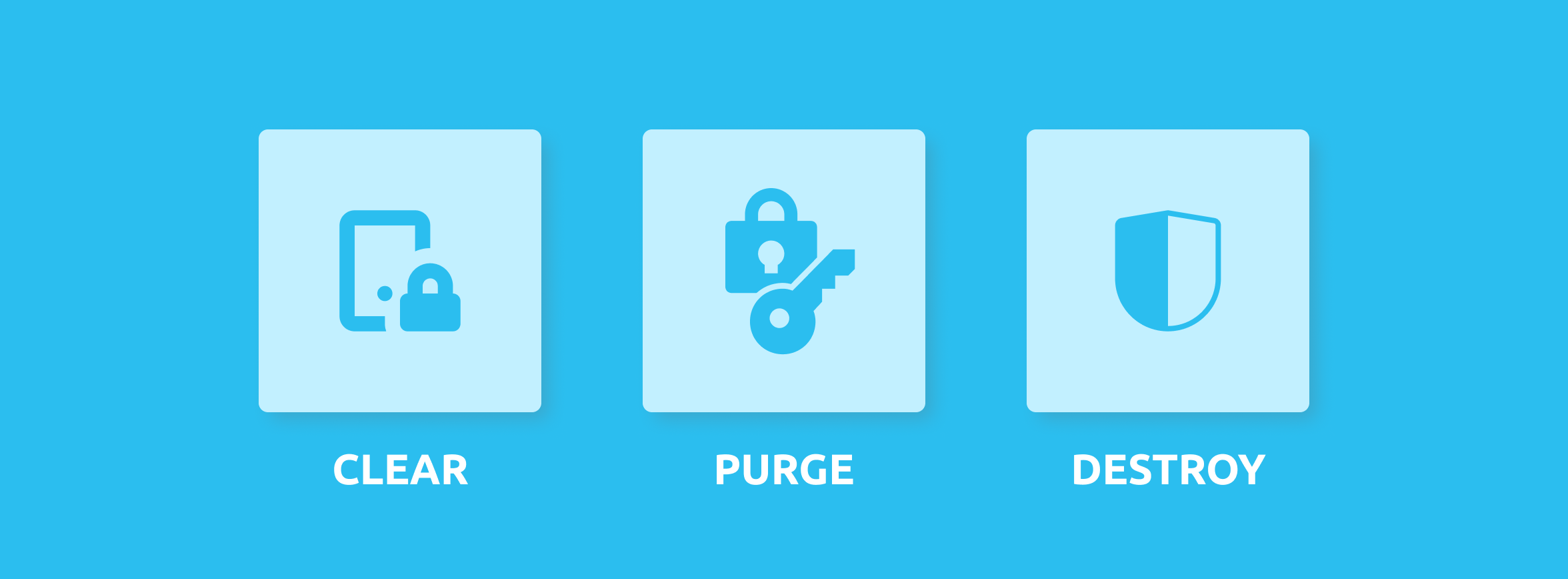
NIST 800–88 provides three methods of dealing with end-of-life data on devices and preventing unauthorized access: clear, purge, and destroy.
- The clear method utilizes techniques to protect data in all user-accessible storage locations. Applied through standard read or write commands, the clear method provides a standard level of data protection against non-invasive data recovery techniques.
- The purge method utilizes techniques that render data unrecoverable. The removal of hidden storage drives triggers a firmware-based command to the drive. The last step verifies the writing on the drive.
- The destroy method utilizes physical techniques like shredding, melting, or incinerating to destroy storage systems and their data, rendering the device unusable and incapable of storing data. The destroy method is often used for devices that are beyond possible use, repair, or overwriting methods because of damage. Purge or clear methods should be tried first, as the destroy method involves the permanent destruction of devices, which can contribute to e-waste.
The History of NIST 800–88 Data Destruction
Published in 2006 with multiple updates since, NIST 800–88 picked up where the DoD 5220.22-M standard left off. NIST 800–88 had its last major update in 2014. It is still the level of data destruction recommended—and sometimes required—by the US Federal Government, superseding the outdated DoD 5220.22-M standards.
The DoD 5220.22-M and NIST 800–88 standards are essential because they affect your company’s data security. They involve preventive action on the data storage systems of your company’s mobile devices, making it more difficult for unauthorized access or worse—data breaches—to occur.
Regardless, a DoD 5220.22-M or NIST 800–88 data destruction process is better than a device factory reset and takes your company data security to the next level, protecting your organization, employees, and customers.
It is also recommended that the process utilized is verified and certified to provide your company with proper audit protection for the future.
Pros and Cons of DoD 5220.22-M and NIST 800–88-Compliant Data Destruction Methods
Department of Defense 5220.22-M-level data destruction sounds very secure and valid. However, it can be misleading, for today’s standards require a higher level of data erasure.
Pros of NIST 800–88 Data Destruction
- NIST 800–88 is the current and updated standard the US federal government recommends.
- NIST 800–88 is a more current process that accounts for recent technologies, technical advancements, and media types while only requiring one overwriting pass.
- NIST 800–88 applies to HDDs, SSDs, and other tech and media types.
Cons of DoD 5220.22-M Data Destruction
- DoD 5220.22-M is an outdated method of data destruction created before smartphones and many of today’s technologies existed. It is also inefficient and costly as it requires three to seven overwriting processes.
- DoD 5220.22-M’s applications limit it to Hard Disk Drive (HDD) storage systems and not the widely-common Solid State Drives (SSD) used in mobile devices.
As the world evolves, so do the cybercriminals wanting access to your valuable company data. Only utilizing DoD 5220.22-M, a 25+-year-old process that hasn’t been updated in almost 15 years, does not provide maximum security for your organization.
Today, NIST 800–88 is the highest standard of data destruction, even for government sectors. Either standard is beneficial, but NIST 800–88 provides the highest level of data protection of the two.
Resources
Want to learn more about DoD 5220.22-M or NIST-800–88-compliant Data Destruction? Check out these resources:
ISO Certification
What is ISO Certification?
The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) is a nonprofit, non-governmental organization consisting of more than 164 governing bodies. The ISO brings together its members and experts from all around the world to share industry knowledge and establish International Standards.
An International Standard is a detailed document that identifies best practices and procedures to implement to solve market-specific challenges.
Following the recognized standards certifies that a system is in place that meets standardization and quality assurance requirements.
An ISO certification ensures an organization is structured and strategic. When an organization adheres to ISO standards, it proves it is credible and committed to improving the quality of its products and services.
ISO standards:
- Ensure products are compatible
- Verify products and services are safe to use or consume
- Share practical information, solutions, and best practices

We may not realize it, but ISO standards play a role in our everyday lives. For example, the food we buy is safe to eat because of food preparation and safety requirements outlined in international standards. Additionally, credit cards can be used virtually anywhere because ISO experts put a best practice in place to standardize payment methods, as every country has its own currency. ISO experts recognized this need and established an international standard for credit cards and card terminals, allowing them to be used globally and recognized as an accepted payment method around the world.
ISO 9001:2015: Quality Management
ISO 9001 is a standard that has a strong customer focus and sets requirements for a quality management system. Establishing an ISO 9001 quality management system can increase an organization’s profitability and overall performance.
ISO 9001 can improve efficiency and customer satisfaction, and it assures businesses that their vendors or suppliers can provide products and services:
- Meeting their needs and expectations
- Complying with applicable international, regional, or local regulations
How ISO 9001 Benefits Customers:
Our third-party processing partner follows ISO 9001, which helps us:
- Set company objectives and goals, allowing us to improve the customer experience
- Ensure we can exceed customer expectations
- Work more efficiently, which can increase productivity and customer satisfaction
- Identify, address, and resolve any potential risks to protect our customers and confidential data
ISO 14001:2015: Environmental Management
ISO 14001 is a standard that helps organizations improve their environmental impact through more efficient use of resources and reducing waste. Establishing an environmental management system allows organizations to gain a competitive advantage.
How ISO 14001 Benefits Customers:
Mobile reCell’s third-party processing partner is ISO 14001 certified, which helps our customers:
- Comply with environmental regulations and/or requirements, while allowing Mobile reCell to analyze and document your IT asset recovery program’s environmental impact
- Protect your organization from reputational damage in the unlikely event of an environmental incident
- Achieve strategic business initiatives by incorporating environmental impact and environmental, social, and governance (ESG) goals in your company’s IT asset recovery programs
- Realize competitive and financial advantages through improved IT asset processing efficiencies
ISO 27001:2013: Information Security Management
ISO 27001 is the most recommended standard for information security management systems (ISMS). ISO 27001 is a detailed set of procedures and requirements that reduces data security risks and ensures confidential information is handled properly.
How ISO 27001 Benefits Customers:
Mobile reCell’s third-party processing partner is ISO 27001 certified, which helps our customers:
- Ensure vendor-specific protection against technology-based risks
- Reduce costs and spending on ineffective processing vendor security practices
- Protect the integrity, confidentiality, and availability of valuable corporate data
ISO 45001:2018: Occupational Health and Safety Management
ISO 45001 applies to all organizations and is recommended for all industries. ISO 45001 is a known standard that controls health and safety risks in a work environment, which helps protect employees from workplace incidents.
ISO 45001 should be integrated into an organization’s existing management processes, as it follows the same high-level structure as other ISO standards and was developed with consideration to the International Labor Organization’s related standard for occupational health and safety management—OHSAS 18001.
ISO 45001 takes a risk-based approach to ensure that the standard is effective and adaptable to meet an organization’s ever-changing needs.
How ISO 45001 Benefits Customers:
Mobile reCell’s third-party processing partner is ISO 45001 certified, which helps our customers:
- Ensure their vendors provide a safe on-site environment for employees, customers, and partners
- Realize increased processing throughput because of reduced processing vendor staff turnover
- Meet and document legal and regulatory requirements related to vendor standards
- Build confidence in processing vendors because of the rapport and improved processing vendor reputations
The Benefits of Working with an ISO-Certified Company
When an organization follows ISO standards, it proves it is committed to achieving its goals while delivering the best customer experience possible. Depending on the industry, following ISO standards may be required instead of just recommended.
Organizations must annually pay, recertify, and undergo audits for ISO certifications to ensure compliance with the standard(s). In some cases, companies undergo training and/or restructure their business to comply with ISO standards.
Mobile reCell works with a third-party processing partner that follows ISO standards to ensure we deliver quality products and services and can meet the growing needs of our customers. Our third-party processing partner is ISO 9001:2015, ISO 14001:2015, ISO 27001:2013, and ISO 45001:2018 certified and upholds several other certifications.
Resources
Want to learn more about ISO Certification? Check out these resources:
- ISO in Brief
- A Brief History of ISO
- ISO: Frequently Asked Questions
- What Exactly is ISO Certified? And Why Does it Matter?
- ISO Standards Agreed by Experts
Encryption and Cryptographic Erasure
What is Encryption?
Encryption is the process of converting device data into a code to prevent unauthorized access. An algorithm then encodes the data so it can only be deciphered with a corresponding encryption key. Essentially, the device’s data is locked away, and a key is provided to unlock it.
As of 2021, only 5% of enterprise devices don’t have encryption enabled.
What is Cryptographic Erasure?
Cryptographic erasure (CE) is one of three methods of handling data, and it is a great option to consider due to its high efficiency and effectiveness.
Cryptographic erasure involves encrypting a device’s stored data first and, when it is time to delete it, discarding the encryption key needed to access that data. A native command is used to erase the encryption key for that stored data, making the device’s storage impossible to decrypt and rendering the data unrecoverable.
The National Institute for Standards and Technology (NIST) and the International Standards Organization (ISO) are two industry data-destruction standards that recommend cryptographic erasure as a secure data destruction technique. This method has also been promoted as a faster alternative to traditional data destruction mechanisms.
The History of Cryptographic Erasure
Cryptographic erasure (CE) dates back to 1996, when it was first publicly proposed in a paper titled “A Revocable Backup System,” published in the USENIX Security Symposium. It involved a backup tape scheme where backed-up data was encrypted with a periodically refreshed key. Every time the key changed, old backups were lost without requiring any modifications to the tape itself.
The Pros and Cons of Cryptographic Erasure
Though a cryptographic wipe is an attractive method to handle data, it has some pros and cons that must be considered.
Pros:
- Cryptographic erasure only takes a few seconds to complete and can be done while devices are in transit or if an organization requires quick handling of data. It is faster than other traditional overwriting methods utilized by the Department of Defense (DoD) or NIST data destruction standards.
- Proper implementation of the process can render data unrecoverable.
- Cryptographic erasure is less expensive than traditional overwriting methods such as DoD 5220.22-M and NIST 800–88.
- Erased devices are still usable after cryptographic erasure, keeping their integrity and retaining warranties, if applicable.
Cons:
- Cryptographic erasure doesn’t actually destroy data; it just makes it inaccessible, meaning future technology could potentially recover the data since it was never destroyed.
- Cryptographic erasure requires all data to be encrypted beforehand, which may not apply to a company’s entire mobile workforce. Companies may be required to integrate this process into their legacy systems, which can be difficult and time-consuming.
- Even when primary encryption keys are deleted, there are often backups to that key, leaving the possibility for a data breach.
- Self-encrypting storage drives can have implementation issues with this process if a company tries to use them.
Overall, cryptographic erasure is a very efficient and effective method of handling data, but understanding its trade-offs is critical if this is the only data-handling method used by a company. For the best results, pair this method with data destruction, like DoD or NIST overwriting methods, to maximize data security.
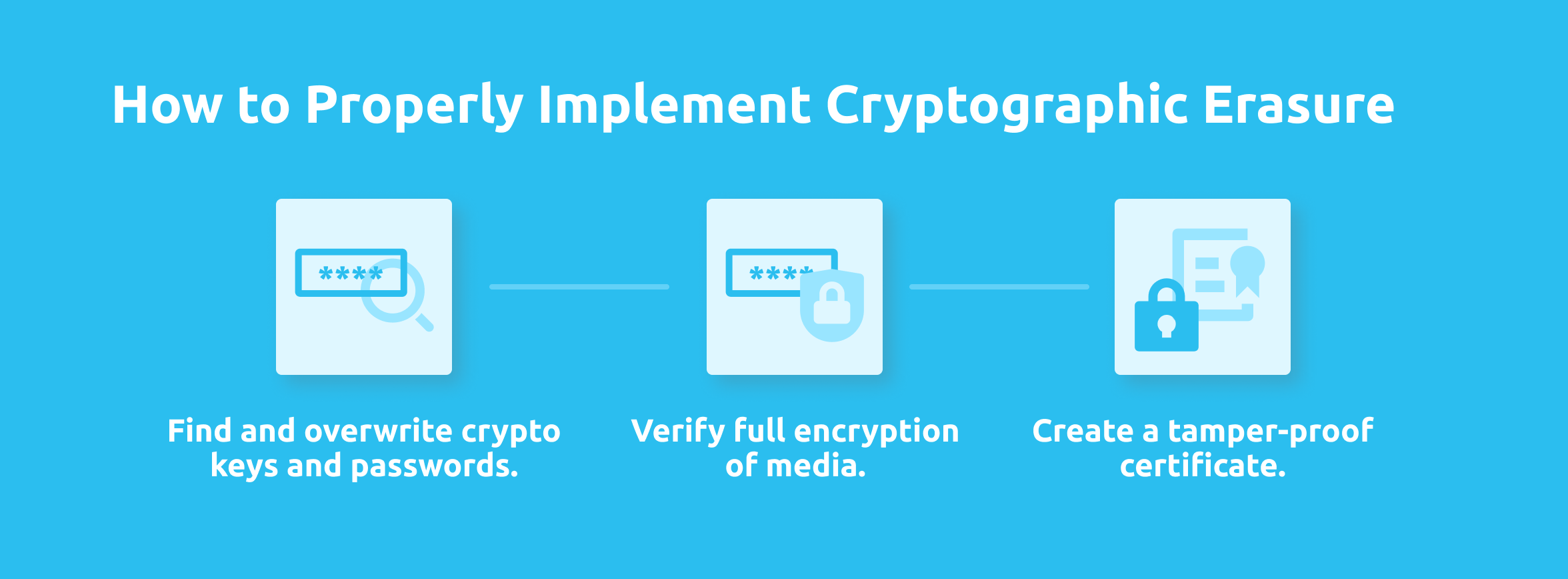
How to Properly Implement Cryptographic Erasure
Assuming the storage device’s data is already encrypted, there are three steps to properly implement cryptographic erasure:
1. Find and overwrite crypto keys and passwords.
- Encrypted storage on a mobile device has its encryption key removed through an API call.
2. Verify full encryption of media.
- Utilized software must verify the old key has been removed and is unrecoverable.
3. Create a tamper-proof certificate.
- The CE software produces the certificate, confirming the encryption key has been removed from a specific device. The certificate is documentation of CE for future data audits.
Reminders for Implementing Cryptographic Erasure
Encrypting data always provides an extra layer of security to your company data, and cryptographic erasure is a proper way to handle encrypted data when corporate-owned devices are retired.
However, cryptographic erasure does not erase data; it simply renders it inaccessible by removing the keys needed to access it. This leaves room for possible data breaches because the data was never destroyed in the first place.
All companies have unique situations and needs, and cryptographic erasure may be the best solution. If encryption keys are managed correctly after devices are retired, it can be a reliable method of handling corporate data.
Cryptographic erasure is a great security option if devices are to stay in your company’s control, but once devices leave the organization or are disposed of, they become vulnerable to unlimited security risks.
If possible, you should always take another step and pair it with another data-overwriting method, like DoD or NIST data destruction, to maximize security. Weighing company risk tolerance and situational needs is critical when considering cryptographic erasure for your company.
Resources for Cryptographic Erasure
Want to learn more about cryptographic erasure? Check out these resources:
e-Stewards
What is the e-Stewards Standard?
The e-Stewards Standard provides visibility into the management and movement of retired IT assets, and is the best and most recommended standard for the responsible recycling and reuse of electronics.
The e-Stewards Standard adheres to strict protocols to ensure devices are handled sustainably and responsibly.
When it comes to discarding electronics, the e-Stewards standard has a system in place to prevent toxic e-waste from being disposed into landfills, exported to the Global South, or recycled using forced labor. e-Stewards conducts unannounced inspections to ensure recyclers are adhering to responsible recycling protocols.
e-Stewards also randomly sends scrap electronic devices with embedded GPS trackers to e-Stewards recycling vendors to ensure companies fulfill their downstream obligations for electronic waste. e-Stewards recycling vendors can purchase more GPS trackers through the EarthEye™ program for their own use, which provides the vendors’ customers with even more confidence that the vendor can account for materials moved downstream.
e-Stewards provides end-to-end accountability throughout the entire recycling process. Working with an e-Stewards certified recycler ensures sustainability is at the forefront of your recycling efforts, protects your organization against risk, and reduces costs.
The e-Stewards Standard for electronics recyclers and IT asset managers requires:
- Secure Data: All data stored on devices must be properly destroyed
- Best Recycling Practices: Recyclers must manage hazardous e-waste following best management practices to protect employees and the environment
- Responsible Downstream Management of All Toxic Materials: e-Stewards recyclers must track all hazardous materials downstream of their facilities
- Ethical Labor: Forced labor is not permitted
- Legal and Responsible Exports: Exporting toxic e-waste to developing countries is forbidden due to international law (Basel Convention)
- Corporate-wide Conformity: All facilities and operations in each country belonging to an organization are certified

Why is the e-Stewards Standard Important?
The e-Stewards Standard is important because it stops the illegal exporting of e-waste to the Global South.
Even though the Basel Action Network (BAN) established an international treaty against the export of toxic waste, e-waste is still often illegally exported to the Global South.
This, unfortunately, includes the United States, as it has not ratified BAN’s international treaty, which means they are not required to follow BAN’s guidelines. The US has virtually no legislation or enforcement in place to prevent e-waste from being shipped overseas.
Working with an e-Stewards certified vendor is essential. They go beyond compliance to ensure electronics are responsibly recycled and provide the best possible asset disposition process.

The History of e-Stewards
The e-waste crisis has been brewing for decades, becoming worse year after year. The e-waste crisis is a critical situation for corporations because, if not addressed, future generations will have to live with the repercussions of e-waste discarded by today’s enterprises, which has already led to a steady decline in our current environmental climate.
A global group of thirteen recycling vendors recognized this issue and discovered how enterprises could minimize the toxic e-waste attributed to their companies—through e-waste recycling. However, the existing e-waste disposal process was not effective.
The group of recyclers discovered that corporations often resorted to exporting e-waste to the Global South without proper approval, contaminating the air and water with harmful chemicals. Exporting e-waste is not a sound solution because it doesn’t solve the issue; it only moves e-waste to another part of the world to be forgotten.
So, they worked to revolutionize the way e-waste is disposed of and recycled.
In 2008, the group of recyclers—later known as the e-Stewards Founders—approached the Basel Action Network (BAN), a non-profit organization creating a sustainable world where society’s discarded items remain a force for good, offering to fund a new standard. The founders wanted a stand-out solution that would differentiate them and ban any export of toxic e-waste to the Global South.
BAN spearheaded the new project, hiring certification experts and bringing in leaders from recycling, asset management, health, and safety sectors to create the e-Stewards Standard—the cleanest, most globally responsible standard for e-waste recycling.
Benefits of Working with an e-Stewards Certified Vendor
Aside from being the highest and strongest standard of e-waste recycling, e-Stewards adheres to National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) standards—specifically a three-step process of guard, sanitize, and test to prevent any risk of legacy data staying on devices after the device is data wiped and resold.
e-Stewards vendors are frequently audited to ensure they follow proper procedures and have systems in place to stay up-to-date on laws surrounding electronic waste and asset disposition—such as HIPAA, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act, and the Privacy Act, which protects consumers’ personally identifiable information (PII).
Committing to work with e-Stewards certified vendors shows that your organization is dedicated to recycling IT assets in the most ethical way possible.
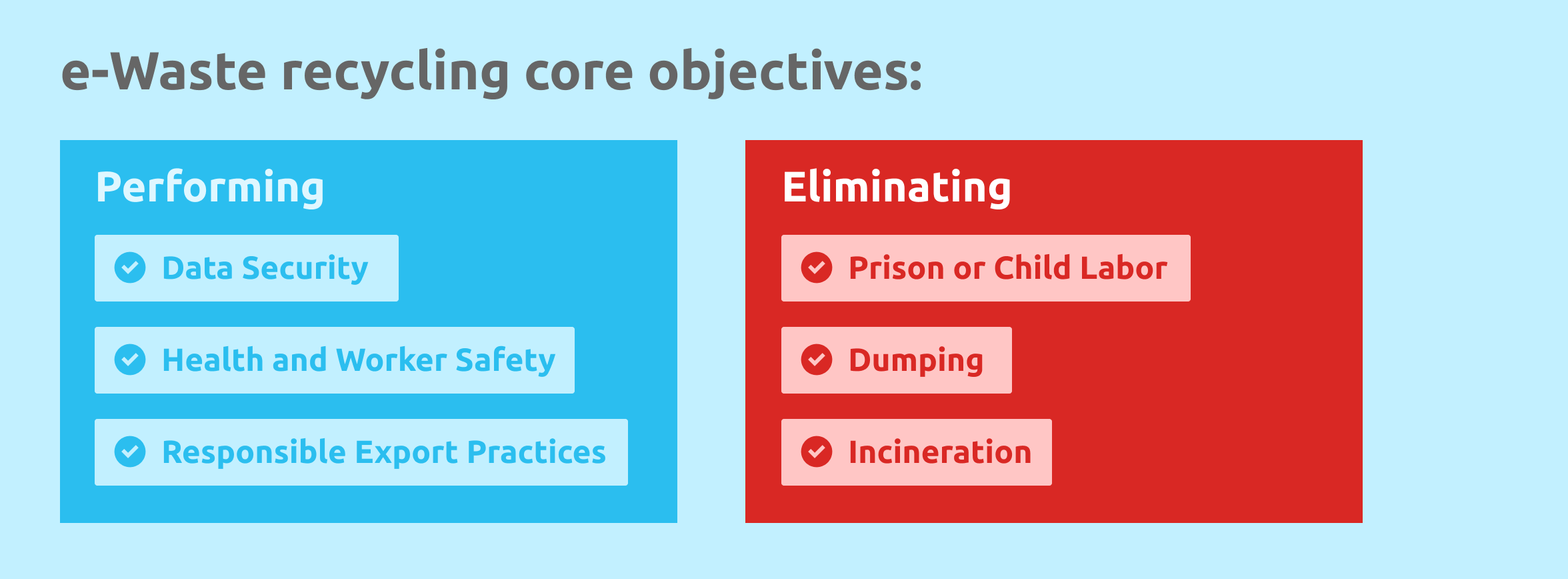
The e-Stewards Standard verifies that e-waste recycling is performed with core objectives of data security, health, and worker safety, responsible export practices, and zero use of prison or child labor, dumping, or incineration. e-Stewards is the only standard that follows all international and local e-waste laws.
Working with e-Stewards certified recyclers also shows your organization is actively working to alleviate the e-waste crisis and its correlating environmental issues, as e-Stewards recyclers can demonstrate the downstream disposition of all hazardous waste throughout their supply chain.
Resources
Want to learn more about e-Stewards? Check out these resources:
SERI and R2 Certification and Guidelines
What are SERI and R2?
Sustainable Electronics Recycling International (SERI) is a nonprofit organization focused on minimizing environmental and health risks posed by used and end-of-life electronics while maximizing the equipment’s social and economic value.
SERI is best known for its Responsible Recycling (R2) standard for electronics, working to reuse and recycle them to preserve resources, the environment, and the health and safety of workers and communities.
Responsible Recycling (R2) results from a collaborative partnership with the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), state agency regulators, electronics recyclers, recycler customers, and Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs), all focused on protecting the environment and companies involved.
R2 is the most widely adopted standard for the responsible reuse and recycling of used electronics. It is easily the most sustainable method of handling end-of-life mobile devices.
R2 keeps electronic waste out of landfills by preserving resources and reducing the need to mine for new materials—reducing the overall human environmental footprint.
R2 Certified facilities help protect the environment while also protecting businesses and their customers from data, health, safety, and environmental risks by issuing specific process requirements.
The History of R2 Certification
Since SERI created its second version in 2013, R2 has been the most popular standard for recycling used and end-of-life devices. There are more than 900 R2 Certified facilities to date, spanning across 28 countries and 13 regions.
Over the years, it has become a truly circular lifecycle for electronics—maximizing value, extending device life, and reusing components or materials whenever feasible.
As of June 2020, R2’s newest version, R2v3, has been recognized as an American National Standard (ANS) by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI), an organization dedicated to enhancing the United States’ quality of life by facilitating standards and ensuring their integrity.
How to Properly Implement R2 Certification
R2 Certification is addressed and audited through specific process requirements:
- Downstream Recycling: Full management of specific equipment and materials.
- Data Sanitization: Physical and logical data destruction to an unrecoverable state.
- Testing & Repair: Extending the life of “working” electronics where possible.
- Materials Recovery: Recovering electronic materials and components like copper, gold, circuit boards, and batteries.
- Specialty Electronics: Coordination with channels and suppliers to reuse commercial-grade, non-consumer electronics.
- Brokering: Responsible for brokering of electronics and parts to downstream vendors.
The Benefits of Partnering with an R2 Certified Vendor
Working with an R2 Certified organization ensures your device recovery program is environmentally responsible and benefits your organization.
With increased health and safety initiatives and proper data destruction on electronics, your organization is protecting its valuable corporate data, customers, employees, and the environment.
R2 Certified partners give your company assurance that your devices are being responsibly reused or recycled at every step possible.
R2 Certified facilities undergo proper education, implementation, evidence, and audits to obtain and maintain their certifications. Frequent audits ensure Certified facilities follow process requirements focused on protecting the environment and companies from which they collect electronics.
Knowing you can trust your chosen partner to handle your end-of-life devices provides your company’s leadership and security professionals peace of mind. Selecting an R2 Certified device recovery partner guarantees customers that their vendor keeps its e-waste out of landfills—often a requirement of organizations’ sustainability initiatives.
Resources
Want to learn more about R2-SERI? Check out these resources:
SOC 2 Type 2
What is SOC 2 Type 2?
System and Organization Controls (SOC) 2 is an examination and report of an organization’s internal security controls developed to help companies determine whether third-party service providers—such as IT asset recovery and disposition vendors—can securely manage customer data.
As organizations grow, they often start outsourcing services that were traditionally fulfilled internally. While outsourcing to third parties can certainly be beneficial by reducing workloads on teams, it can also be risky.
If an organization experiences a data breach because of a third-party service provider’s inability to ensure security, the organization is forced to pause business operations to recover and may lose revenue and customers as a result.
Organizations must ensure any third-party service providers or vendors accessing or handling their data meet specific security standards, minimizing the exposure of valuable corporate data.
SOC 2® was developed by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA), and the examination and auditing processes are split into two types of SOC 2 reports:
- SOC 2 Type 1: A snapshot of a service organization’s internal controls at a single point in time.
- SOC 2 Type 2: Examines a service organization’s internal controls to secure and protect customer data over a duration of time.
The History of SOC 2 Type 2
SOC 2 was first introduced in 2010 by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) to make its existing criteria for financial risk audits more tech-friendly.
As organizations became increasingly reliant on technology and expensive infrastructure, the AICPA developed controls in its original audit framework (SAS 70) to ensure asset values were not compromised. These new controls resulted in a new auditing standard superseding SAS 70—the Statement on Standards for Attestation Engagement (SSAE 16).
The SSAE 16 includes three reports:
- SOC 1: Report on controls at a service organization relevant to the user entity’s internal control over financial reporting
- SOC 2: Report on controls at a service organization relevant to security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, or privacy
- SOC 3: Trust Services Criteria for general use
In 2017, SSAE 16 was replaced with SSAE 18 by the AICPA. Today, SSAE 18 is used for all SOC 1, SOC 2, and SOC 3 audits and attestation reports.

How to Conduct a SOC 2 Type 2 Examination
A SOC 2 examination is “an examination of a service organization’s description of its system, the suitability of the design of its controls, and, in a Type 2 examination, the operating effectiveness of controls relevant to security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, or privacy.”
SOC 2 Type 2 is notably one of the most complex security examinations to endure due to its comprehensive and time-consuming process.
To conduct a SOC 2 Type 2 examination, organizations must select the Trust Services Criteria (TSC) tailored to the controls they have in place and wish to examine. Established by the AICPA, the TSC consists of security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy.
- Security: Focuses on protecting the assets and data of the service to ensure adherence to SOC 2 Type 2 standards against unauthorized use. Organizations can implement access controls to prevent malicious attacks or unauthorized removal of data, misuse of company software, unsanctioned alterations, or disclosure of company information.
- Availability: Focuses on the accessibility of data and systems used to meet business objectives. Assesses an organization’s maintenance by monitoring data, infrastructure, and software.
- Processing Integrity: Focuses on ensuring organizations deliver the correct data at the right time. System processing should be complete, valid, accurate, authorized, and timely. This category also identifies if the established systems fulfill an organization’s set objectives and perform correctly—free from error, delay, or manipulation.
- Confidentiality: Focuses on restricting access and disclosing private data to ensure only specific people or organizations can view it. Confidential data may include sensitive business and financial information, customer data, trade secrets, or intellectual property. Confidentiality requirements may be outlined in laws, regulations, or contracts making commitments to customers or others.
- Privacy: Focuses on the system’s adherence to customers’ privacy policies and the Generally Accepted Privacy Principles (GAPP) from the AICPA. This category examines the methods used to collect, use, and retain personal information and the process for disclosure and disposal of data.
The Benefits of Seeking Vendors with Clean SOC 2 Type 2 Reports
Remedying a corporate data breach generates high financial costs and hinders growth due to a loss in productivity. One of the simplest ways to mitigate those costs is only working with third-party service providers willing to offer proof of a clean SOC 2 Type 2 report.
A clean SOC 2 Type 2 report assures your IT and business leaders that third-party service providers—like Mobile reCell—have adequate security controls in place around infrastructure, software, people, and processes for the protection and privacy of your company’s sensitive data.
The need for SOC 2 reporting is also driven by newer regulations requiring data protection and privacy, such as General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA).
Some government agencies and organizations require third-party service providers to obtain a clean SOC 2 audit report as part of their contract agreements.
A clean SOC 1 report demonstrating internal controls around financial reporting and a clean SOC 2 report indicating the safe handling of valuable company data help to fulfill Sarbanes-Oxley requirements for public companies.
Mobile reCell has implemented the strictest security standards to protect our customers and minimize the risk of a data breach.
Mobile reCell has officially received its first clean SOC 2 Type 2 attestation report, which is now available upon request.
Resources
Want to learn more about SOC 2 Type 2? Check out these resources:
Data security is a priority for Mobile reCell, and enterprise-grade data protection keeps your valuable corporate data secure and meets your compliance requirements.
We are dedicated to ensuring adherence to industry standards with documented and transparent compliance.
Contact us for assistance with implementing a secure, transparent, and sustainable IT solution for your IT asset recovery program.
